In JMeter, JSR223 Listener is a scripting-based listener. JSR stands for Java Specification Requests. As same as BeanShell Listener which we discussed earlier; you will need to implement the listener logic by yourself using one of the supported scripting languages like Groovy, BeanShell, java, javascript, jexl etc. Usually, it is helpful when you need to write custom code based on some unique algorithm which is not currently provided by JMeter. You can create your own implementation of the code using the JSR223 Listener.
How to add ‘JSR223 Listener’?
You can follow the below steps:
- Select the appropriate element where you want to add the listener
- Test Plan
- Thread Group
- Controller
- Sampler
- Right-click on the element
- Hover the cursor on ‘Add’
- Hover the cursor on ‘Listener’
- Click ‘JSR223 Listener’
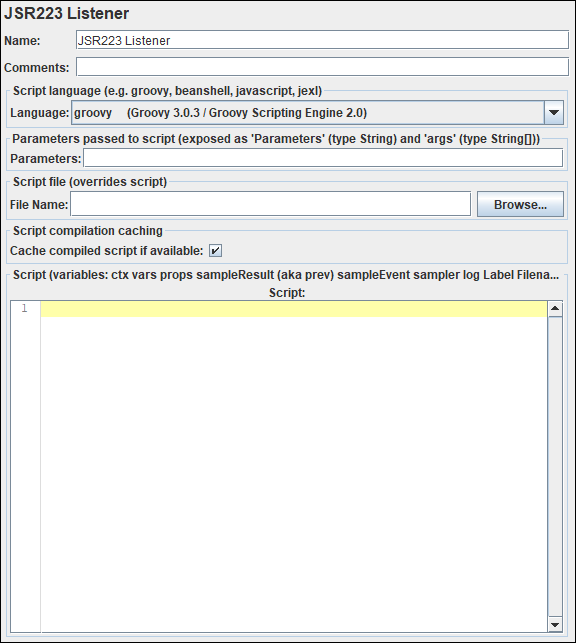
What are the input fields of ‘JSR223 Listener’?
‘JSR Listener’ has the following input fields:
- Name: To provide the name of the post-processor
- Comments: To provide arbitrary comments (if any)
- Language: To choose the scripting language.
- Parameters: Parameters to pass to the script. This is an optional attribute.
- Script file: A file containing the script to run. The return value is the desired output.
- Script compilation caching: Unique String across Test Plan that JMeter will use to cache the result of script compilation if the language used supports Compilable interface (Groovy is one of these, java, BeanShell and javascript are not)
- Script: The manual script which contains the listener logic.
Recommendation: It is recommended to use JSR223 test elements and Groovy as a language for any scripting. Groovy scripting is as fast as Java while BeanShell and JavaScript need to be interpreted, which causes some performance overhead.

